Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
What is eczema?
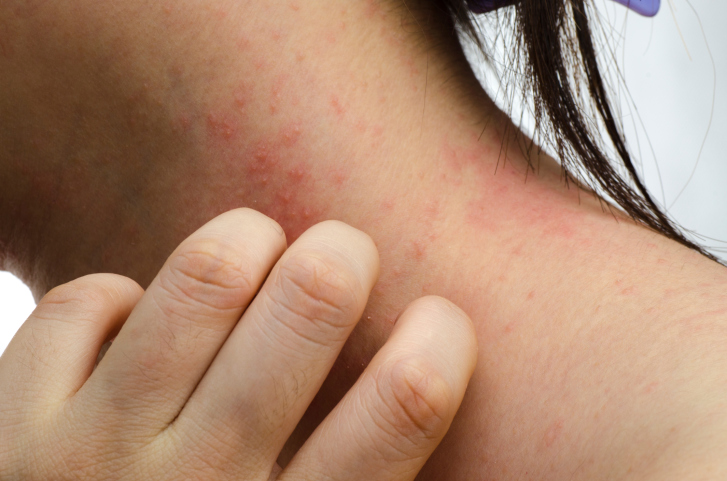
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a common skin condition affecting 1 in 5 children. It may present at any age but is more common in childhood and adolescence.
What is the treatment for eczema?
Unfortunately there is no cure for eczema. In many cases eczema will improve over time, however in a small number of cases it may persist into adulthood.
General skincare measures are an essential component in managing eczema. Often a small change to a daily skincare regime will significantly improve the symptoms and severity of eczema.
Important general measures include:
- Avoidance of hot water and overheating
- Avoid soap containing products
- Moisturise the skin regularly
- Wear soft clothing (in general avoid woollen products)
Prescription topical treatments include:
- Topcial steroids
- Calcinurin inhibitors (pimecrolimus or tacrolimus)
Phototherapy
- A form of narroband UVB light treatment
In more severe cases a longer term systemic immunosuppressive agent will be required. These are usually prescribed under the supervision of a dermatologist:
- Methotrexate
- Azathioprine
- Cyclosporine
What is the "best" moisturiser?
In my opinion there is no "best" moisturiser. I often say to my patients that the "best" moisturiser is one they will actually use regularly.
In general, greasy moisturisers will hydrate the skin more and improve the barrier function of the skin. However often the greasy moisturisers are less convienient to use during the day and so they are reserved for more severe cases or when the skin has flared. The less greasy moisturisers are more suited to daily use to keep the skin moisturised and prevent eczema coming back.
Examples of greasy moisturisers include:
- QV intensive
- Dermeze
- 10/10/10 (a specially compounded moisturiser incorporating 10% white soft paraffin, 10% liquid paraffin and 10% glycerine in an aqueous cream base)